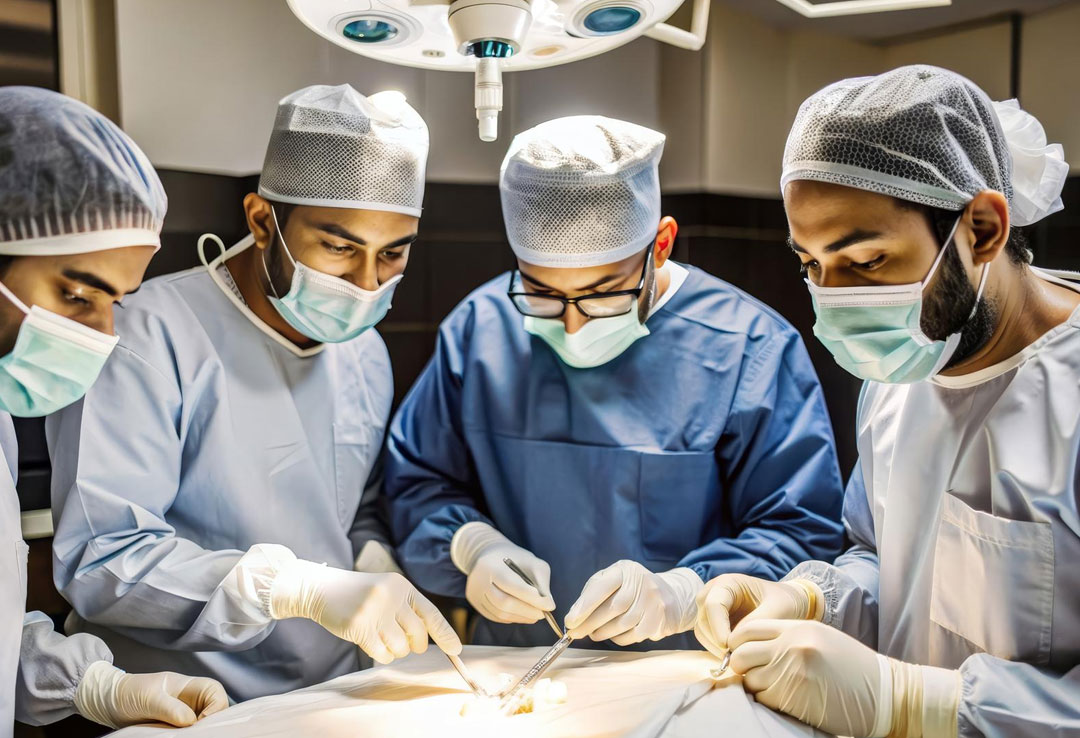
Minimally invasive surgical procedures for diagnosing and treating reproductive health issues, such as endometriosis and fibroids
Laparoscopy, also known as “keyhole surgery,” is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat various conditions within the abdominal and pelvic areas. During the procedure, a small incision is made in the abdomen, through which a laparoscope—a thin tube with a light and camera—is inserted. This allows the surgeon to view the internal organs on a monitor and identify issues such as endometriosis, ovarian cysts, fibroids, pelvic inflammatory disease, and other reproductive system disorders.
In addition to diagnosis, laparoscopy can be used for therapeutic purposes, such as removing cysts or fibroids, treating ectopic pregnancies, or performing tubal ligation. The advantages of laparoscopy over traditional open surgery include smaller incisions, less pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times. It is often performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to resume normal activities in a shorter time frame. This makes laparoscopy a preferred choice for many gynecological and abdominal procedures.